20919 - The efficiency of combustion of methane
E. Conophagos, N. Lygeros
Translated from the Greek by Athena Kehagias
Methane belongs to the family of alkanes, which follows the following equation: CnH2n+2.
To the same family also belong the ethane, the propane and the butane, which are gaseous.
From the pentane and thereafter we have liquid form.
The combustion of methane gives water and carbon dioxide and has the following equation: CH4+2O2 -> CO2+2H2O + heat.
We see that for one molecule of methane, we have one molecule of carbon dioxide.
This output is of course different in regards to the other alkanes, for which we have the general equation: CnH2n+2 + (3n+1)/2 O2 -> n CO2 + (n+1) H2O with simultaneous heat production.
This means that the methane combustion is the more effective as far as the minimizing of carbon dioxide production is concerned.
In alkanes we observe it clearly, as the increase is linear.
So we see therefore, that its combustion contributes even more in minimizing the greenhouse effect, because, firstly it avoids its existence in the atmosphere, because it is 30 times worse than carbon dioxide and secondly we convert it to carbon dioxide with the minimum quantity.
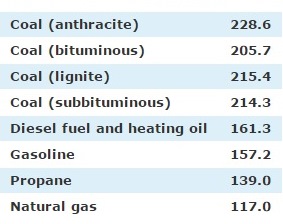
If now we were to generalize the problem, and to compare it with other combustion products, it would be methane again which produces less carbon dioxide.
That’s what we see in the following table.
Therefore the methane with its combustion, is the most effective, not only because it produces the highest heat, but also the minimum carbon dioxide.